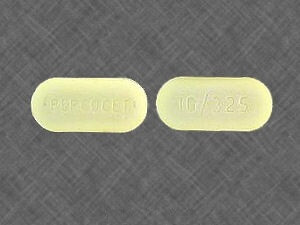
Percocet: Comprehensive Guide to Uses, Risks, and Alternatives
Percocet, a combination of oxycodone (an opioid pain reliever) and acetaminophen (a less potent painkiller), is commonly prescribed for managing moderate to severe pain. While it is effective in pain relief, Percocets comes with significant risks, including addiction and overdose. In this guide, we’ll explore how Percocets works, its uses, side effects, and safer alternatives for pain management.
What Is Percocet?
Percocets is a prescription medication that contains two active ingredients:
- Oxycodone: A powerful opioid that relieves pain by blocking pain signals in the brain.
- Acetaminophen: A non-opioid analgesic that enhances the pain-relieving effects of oxycodone while reducing fever.
Percocets is typically prescribed when other pain relief methods, like non-opioid analgesics, have been ineffective.
Common Uses of Percocet
- Pain Relief: Percocets is often prescribed for moderate to severe pain caused by injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions where other medications have not worked.
- Post-Surgical Pain: After surgery, Percocets is used to manage discomfort, helping patients recover more comfortably.
How Percocet Works
Oxycodone in Percocets binds to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals, while acetaminophen works to reduce inflammation and alleviate fever. This combination provides effective pain relief for a variety of conditions.
Side Effects of Percocet
While effective, Percocets can cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness or dizziness
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
Serious side effects may include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Liver damage (from acetaminophen overdose)
- Risk of addiction and overdose
If you experience symptoms like confusion, slow breathing, or yellowing of the skin or eyes, seek immediate medical attention.
Risks and Safety Precautions
Addiction and Overdose: Percocets contains oxycodone, which has a high potential for addiction, misuse, and overdose. Using Percocets in higher doses than prescribed, or mixing it with alcohol or other sedatives, can lead to fatal consequences. Never share Percocets with others, and always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Liver Damage: Acetaminophen in Percocets can cause liver damage if taken in excessive amounts. Always be mindful of the recommended dose to avoid toxicity.
How to Take Percocet Safely
- Dosage: Always take Percocets as prescribed. Do not exceed the recommended dose, and never crush or break the tablets.
- Storage: Store Percocet at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Keep it out of reach of others, particularly children, to prevent accidental overdose.
Alternatives to Percocet
If you’re concerned about the risks associated with Percocet, consider these alternatives:
- Non-Opioid Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be sufficient for managing mild to moderate pain.
- Physical Therapy: For chronic pain conditions, physical therapy can be an effective way to manage pain without relying on medications.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs can provide relief for pain caused by inflammation, such as arthritis.
Conclusion
Percocet is an effective option for short-term pain relief, but its potential for addiction, overdose, and liver damage makes it important to use only as prescribed. If you or a loved one is prescribed Percocet, always follow the doctor’s instructions carefully, and never hesitate to ask about safer alternatives.
For more information on Percocet or to explore pain management options, visit for trusted advice and expert insights.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.